Plastic surgery has evolved far beyond reshaping appearance alone. Today, equal emphasis is placed on how the body heals after surgery, how tissues regenerate, and how long-term results can be optimized. As a result, regenerative medicine has become an area of growing interest within plastic surgery, particularly for its potential to support recovery and tissue quality rather than replace surgical techniques.
One emerging area within this field is exosome therapy. Exosomes have gained attention for their role in cellular communication and their potential to influence healing and regeneration processes. In plastic surgery, exosome therapy is being explored as a supportive treatment that may help modulate inflammation, encourage tissue repair, and improve the overall healing environment following surgical procedures.
In this article, we explain what exosomes are, why they are attracting attention in plastic surgery, how they work at the cellular level, and what role they may play in supporting healing and tissue regeneration. We also discuss safety considerations, current limitations, and what patients should know before considering exosome-based treatments as part of their surgical journey.
What Are Exosomes?
Exosomes are microscopic, membrane-bound particles released naturally by cells throughout the body. Their primary function is communication. They carry biological signals from one cell to another, helping coordinate responses such as inflammation control, tissue repair, and regeneration.
Each exosome contains a mix of bioactive molecules, including proteins, lipids, and genetic material such as RNA. When these signals are delivered to a target cell, they can influence how that cell behaves, particularly in response to injury or stress.
It is important to distinguish exosomes from stem cells. Exosomes are not living cells and do not form new tissue themselves. Instead, they act as messengers that influence existing cells. This makes them interested in plastic surgery, where controlled tissue injury occurs and coordinated healing is essential.

Why Exosome Therapy Is Gaining Attention in Plastic Surgery
Exosome therapy has entered this discussion because of its role in cellular communication and regenerative signaling. Rather than altering anatomy or replacing surgical techniques, it is being explored as a supportive approach that may help create a more favorable healing environment following controlled tissue trauma.
Several factors contribute to the growing attention around exosome therapy in plastic surgery:
- Increased emphasis on recovery quality and tissue regeneration after surgery
- Interest in regenerative medicine that supports healing without introducing living cells
- Demand for adjunctive treatments that may complement established surgical techniques
- Ongoing research into inflammation modulation and collagen organization
- Patient interest in advanced recovery-support options alongside surgery
How Exosome Therapy Works at the Cellular Level
Exosomes function as messengers between cells, carrying signals that help coordinate how tissues respond to injury and repair themselves. In the context of plastic surgery, this cellular communication is relevant because surgical procedures intentionally disrupt skin, connective tissue, and blood vessels as part of reshaping and reconstruction.
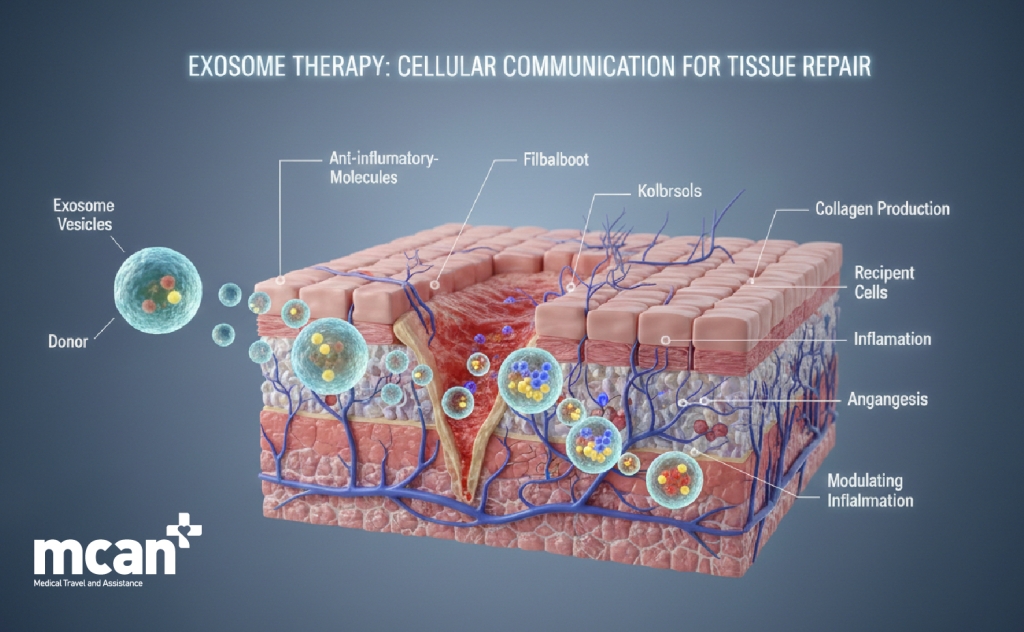
When tissue is injured, the body initiates a complex healing response involving inflammation, cell migration, collagen production, and new blood vessel formation. Exosomes are involved in regulating these processes by delivering molecular instructions that influence how cells behave during healing.
At a cellular level, exosome signaling may contribute to healing by:
- Modulating inflammatory responses, helping prevent prolonged or excessive inflammation
- Supporting fibroblast activity, which plays a role in collagen production and tissue strength
- Encouraging organized tissue repair rather than irregular scar formation
- Supporting communication between skin cells, connective tissue cells, and blood vessels
- Influencing angiogenesis, the formation of new blood vessels needed for tissue recovery
Potential Benefits of Exosome Therapy in Plastic Surgery
The potential role of exosome therapy in plastic surgery is closely tied to how the body manages healing after surgical intervention. Surgery intentionally creates controlled tissue injury, triggering inflammation, repair, and collagen remodeling. The way these processes unfold influences scar quality, tissue texture, and how results settle over time.
Areas where exosome therapy may offer supportive benefits include:
- Inflammation regulation: Exosome signaling may help guide inflammatory responses so they resolve appropriately rather than remaining prolonged, which can interfere with healing and comfort.
- Tissue repair coordination: By influencing communication between skin cells, fibroblasts, and blood vessels, exosomes may support more orderly tissue regeneration during recovery.
- Collagen organization: Collagen is essential for healing, but how it is laid down matters. Exosome-related signaling may encourage structured collagen formation rather than irregular or dense buildup.
- Skin behavior during healing: Some research suggests exosomes may support healthier skin response during recovery, potentially influencing texture and resilience as tissues heal.
These effects, when present, tend to be subtle and vary between individuals. Factors such as surgical extent, tissue quality, overall health, and post-operative care play a far greater role in determining recovery outcomes.
For this reason, exosome therapy should be viewed as a supportive adjunct, not a corrective treatment. It does not eliminate scars, prevent complications, or replace surgical precision. Instead, its potential value lies in helping the body manage healing more effectively within the limits of natural biology.
How Exosome Therapy Can Be Used Around Plastic Surgery
In plastic surgery, exosome therapy is not positioned as a standalone treatment but as a supportive option that can be integrated around the surgical process. Its role is to complement surgical care by supporting the biological environment in which healing and tissue regeneration occur.
The way exosome therapy is used depends on the type of procedure, timing, and overall treatment plan. Rather than being applied uniformly, it is typically considered as part of a broader recovery and tissue support strategy.
Exosome therapy can be used in several ways around plastic surgery procedures:
- During the post-operative healing phase: After surgeries such as tummy tuck, breast surgeries, or facelift procedures, exosome therapy can be applied during early recovery to support tissue repair when inflammation and cellular activity are most active.
- As an adjunct to facial surgery: In facial procedures including facelift surgery, eyelid surgery, or neck lift surgery, where skin quality and scar maturation are especially important, exosomes can be incorporated to support softer healing and tissue adaptation.
- Alongside body contouring procedures: Following body contouring treatments such as liposuction, body lift surgery, or arm lift and thigh lift, exosome therapy can be used to support organized healing across larger treatment areas that involve significant skin and tissue manipulation.
- With skin-focused aesthetic treatments: Exosomes can be combined with skin rejuvenation treatments such as laser resurfacing, microneedling, or chemical peels performed around the time of surgery to support surface-level recovery and overall skin quality.
- Through different delivery methods: Depending on the clinical approach and treatment area, exosomes can be applied topically or delivered through injections, with the method selected based on surgical goals, tissue depth, and recovery needs.
Exosome Therapy vs Other Regenerative Approaches
Exosome therapy is often discussed alongside other regenerative treatments used in aesthetic and plastic surgery, particularly platelet-rich plasma (PRP) and stem cell–based therapies. While these approaches share a common goal of supporting healing and tissue quality, they differ significantly in how they work, how they are obtained, and how they are used clinically.
The table below highlights key differences between these approaches:
| Aspect | Exosome Therapy | PRP (Platelet-Rich Plasma) | Stem Cell–Based Therapies |
|---|---|---|---|
| Source | Derived from cultured cells | Patient’s own blood | Patient’s tissue or donor sources |
| Contains living cells | No | No | Yes |
| Primary function | Cellular signaling support | Growth factor release | Cell replacement and regeneration |
| Invasiveness | Low | Low (blood draw required) | Higher (tissue harvesting required) |
| Role in plastic surgery | Supportive adjunct to healing | Supportive adjunct to healing | More complex regenerative use |
| Predictability of outcomes | Variable | Variable | Highly variable |
| Regulatory complexity | Evolving | Well established | Highly regulated |
| Replacement for surgery | No | No | No |
While PRP relies on growth factors released from platelets and stem cell therapies involve living cells capable of differentiation, exosomes function as biological messengers. Their role is to influence how existing cells behave during healing rather than to directly rebuild tissue or add volume.
Safety, Regulation, and Current Limitations
As interest in exosome therapy grows, questions around safety, regulation, and clinical reliability become increasingly important. While exosomes are naturally occurring in the body, their therapeutic use in plastic surgery requires careful consideration of how they are sourced, processed, and applied.
From a safety perspective, exosome therapy is generally positioned as low risk when handled correctly. Because exosomes are non-living vesicles rather than whole cells, they do not divide or integrate into tissue in the way stem cells do. However, safety is closely tied to quality control and clinical protocols rather than the concept of exosomes alone.
Key safety and regulatory considerations include:
- Source and processing standards: The biological source of exosomes and the methods used to isolate and preserve them play a critical role in safety. Poor sourcing or inadequate processing can compromise consistency and effectiveness.
- Product variability: Not all exosome products are the same. Differences in cell origin, concentration, and preparation methods can lead to variable biological activity and inconsistent results.
- Regulatory status: Exosome therapies exist in a regulatory gray area in many regions. While research and clinical exploration are ongoing, standardized regulatory approval pathways are still developing.
- Limited long-term data: Much of the available evidence comes from laboratory studies, early clinical research, or short-term observations. Large-scale, long-term clinical trials are still needed to fully understand outcomes and risks.
- Dependence on clinical context: Exosome therapy does not function independently of surgical technique or post-operative care. Its effectiveness is influenced by how, when, and why it is used within a broader treatment plan.
Who May Be Considered for Exosome Therapy in Plastic Surgery
Exosome therapy is not intended for every plastic surgery patient, nor is it automatically appropriate simply because surgery is being performed. Its use is typically considered on a case-by-case basis, depending on the patient’s goals, health status, and expectations around recovery support.

In plastic surgery, exosome therapy is most often discussed as an option for patients who are interested in supporting healing quality rather than altering the surgical plan itself. The focus is on biological support during recovery, not on changing the scope or outcome of the procedure.
Patients who may be considered for exosome therapy include:
- Individuals undergoing elective plastic surgery: Patients having planned aesthetic procedures may consider exosome therapy as part of a broader recovery-support strategy.
- Patients focused on healing quality and tissue health: Those who are particularly concerned about inflammation control, skin behavior, or scar maturation may find exosome therapy aligns with their priorities.
- Patients with realistic expectations: Exosome therapy is best suited for individuals who understand that it supports healing processes rather than delivering visible or immediate aesthetic changes.
- Patients interested in regenerative approaches: Individuals who are open to emerging regenerative technologies, while accepting that evidence is still evolving, may be appropriate candidates.
What Exosome Therapy Cannot Do
As interest in exosome therapy continues to grow, it is equally important to understand its limitations. Clear boundaries help prevent unrealistic expectations and ensure that exosome therapy is viewed appropriately as a supportive option rather than a solution in itself.
Exosome therapy does not change the fundamentals of plastic surgery. It works within the limits of the body’s natural healing capacity and cannot override surgical technique, anatomy, or individual biology.
Exosome therapy cannot:
- Replace plastic surgery procedures: Exosomes do not tighten skin, remove excess tissue, reposition structures, or create volume. Surgical correction remains essential for achieving structural or aesthetic change.
- Guarantee faster or complication-free healing: While exosomes can support biological processes, they cannot eliminate risks such as swelling, bruising, infection, or delayed healing.
- Prevent or erase scars: Scarring is a natural part of healing after surgery. Exosome therapy cannot eliminate scars or ensure a specific scar outcome, as scar formation is influenced by genetics, incision placement, and aftercare.
- Correct surgical errors or poor technique: No regenerative therapy can compensate for inadequate surgical planning or execution. Precision, experience, and proper technique remain the primary determinants of outcome.
- Override individual healing differences: Patients heal differently based on age, health, skin quality, circulation, and lifestyle factors. Exosome therapy cannot standardize or equalize these biological differences.
- Deliver immediate visible aesthetic changes: Any supportive effects occur gradually during healing and are not associated with instant or dramatic visual improvement.
Exosome Therapy in Plastic Surgery with MCAN Health
Turkey has become an established destination for advanced plastic surgery, and interest in regenerative support treatments such as exosome therapy continues to grow among international patients. At MCAN Health, exosome therapy is approached as a supportive option rather than a standalone solution, carefully considered in relation to surgical planning, healing goals, and individual patient biology.

Patients choose MCAN Health when exploring exosome therapy alongside plastic surgery in Turkey for several key reasons:
- Experienced Plastic Surgeons: MCAN Health works with board-certified surgeons who understand both surgical technique and post-operative tissue behavior, allowing exosome therapy to be considered only when it aligns appropriately with recovery needs.
- Accredited Surgical Facilities: All treatments are delivered within TEMOS-accredited and internationally certified hospitals that meet strict safety, hygiene, and clinical standards.
- Structured Treatment Experience: Surgical care, accommodation, transfers, medications, and in-hotel nurse visits are coordinated to support controlled recovery rather than rushed intervention.
- Multilingual Patient Support: A multilingual care team ensures clear communication and informed decision-making at every stage of treatment.
- UK-Based Aftercare Office: Continued follow-up is available after patients return home, allowing healing progress and long-term recovery to be monitored with confidence.
A Measured Approach to Regenerative Support
MCAN Health’s care model emphasizes realism and responsibility when integrating emerging therapies:
- MCANCare: Nurse-led support during the early recovery phase, with attention to wound care, comfort, and healing progress.
- MCANFollow: A structured 12-month follow-up program designed to observe recovery over time rather than focus on immediate outcomes.
- MCANAssurance: Reassurance through transparent care pathways in the unlikely event that additional support is required.
With MCAN Health, exosome therapy in plastic surgery is considered through a clinical lens rather than a marketing one. The focus remains on safe surgery, predictable healing, and long-term tissue health, with regenerative options introduced only when they support those goals in a meaningful way.
 What Is Exosome Hair Treatment? Benefits, Safety and How It Works
What Is Exosome Hair Treatment? Benefits, Safety and How It Works  PP405 Hair Loss Treatment: What It Is, How It Works, and What to Know
PP405 Hair Loss Treatment: What It Is, How It Works, and What to Know  Circumferential Tummy Tuck Explained: How It Works and Who May Benefit
Circumferential Tummy Tuck Explained: How It Works and Who May Benefit