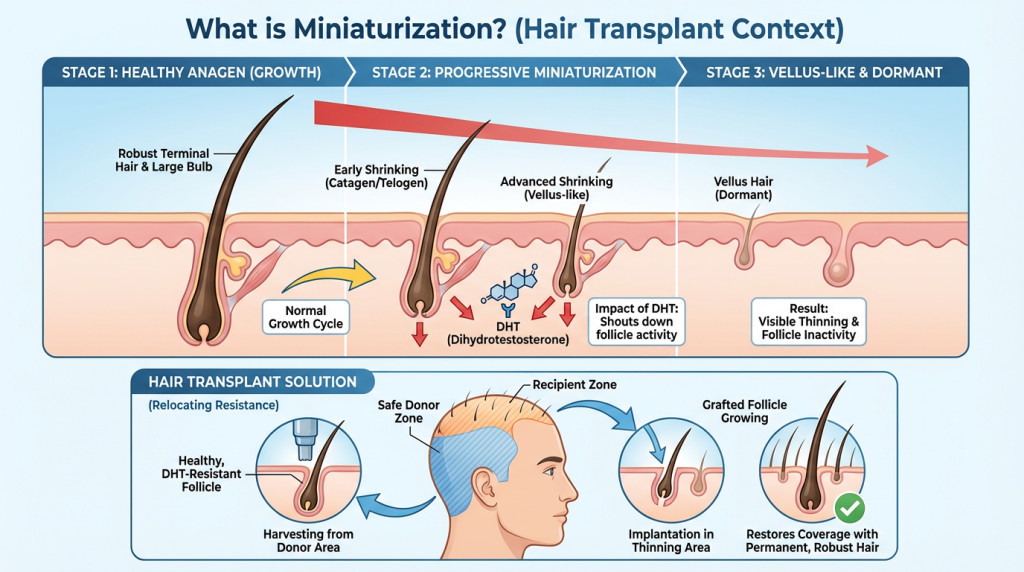
Miniaturization
Miniaturization describes the gradual shrinkage of hair follicles that leads to successive hairs becoming finer, shorter and often less pigmented. It commonly reflects a shortening of the anagen (growth) phase and a shift toward vellus-like hairs, typically driven by genetic predisposition and increased sensitivity to androgens such as dihydrotestosterone.
Clinically, miniaturization is the primary mechanism behind visible thinning in pattern hair loss and can be assessed with tools like trichoscopy, hair diameter measurement or biopsy; a high proportion of miniaturized hairs indicates active progression. Understanding the extent of miniaturization helps guide treatment decisions—medical therapies aim to halt or partially reverse follicle shrinkage, while surgical options such as hair transplantation are considered when progression is controlled and adequate donor hair is available.