Breast Ptosis (Sagging)
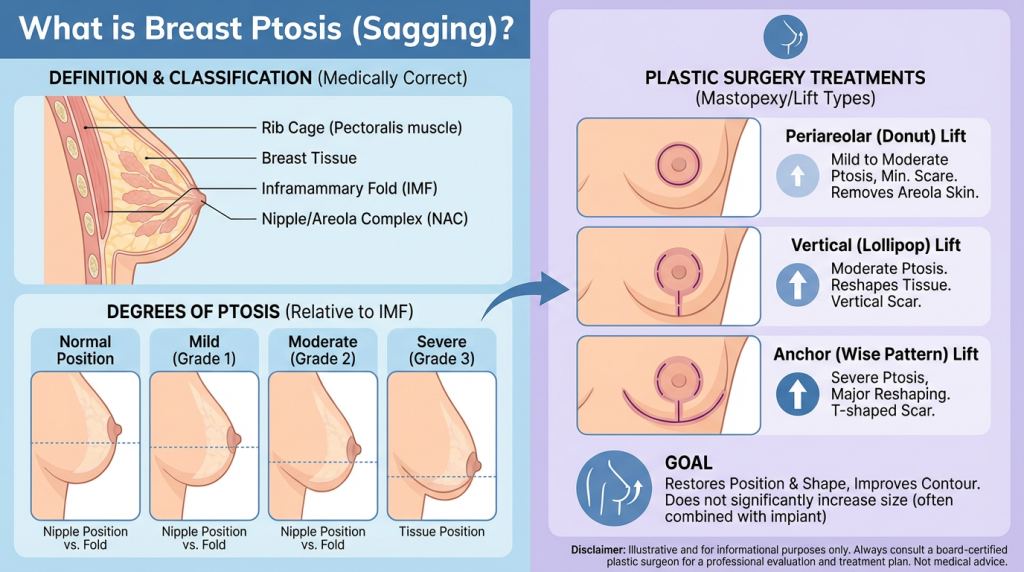
Breast ptosis (sagging) refers to the descent of the breast tissue and nipple-areola complex relative to the inframammary fold and chest wall. It most commonly develops from aging, gravity, pregnancy and breastfeeding, weight fluctuations, loss of skin elasticity, and genetic factors, and is often categorized clinically as mild, moderate, or severe based on the position of the nipple in relation to the inframammary fold.
Evaluation by a plastic surgeon includes breast size, skin quality, nipple position and patient expectations; while supportive garments and lifestyle measures can improve comfort, they generally cannot reverse ptosis. Surgical correction, typically a mastopexy (breast lift) and sometimes combined with augmentation or reduction, repositions and reshapes the breast; patients should understand likely scars, recovery timelines, potential changes in sensation, and risks such as asymmetry or the possibility of revision procedures.