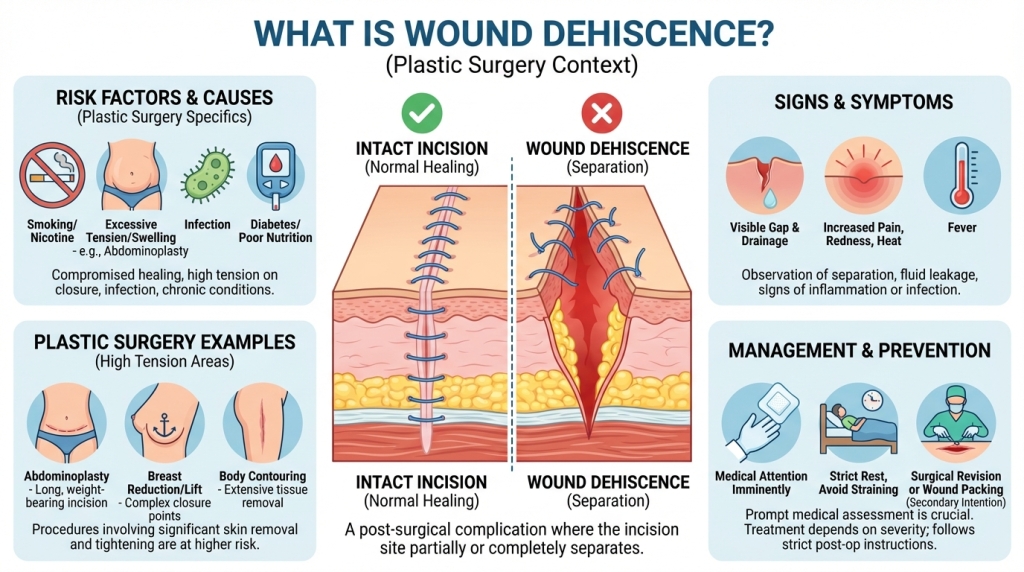
Wound Dehiscence
Wound dehiscence is the reopening of a surgical incision or wound after it has been closed, and it can range from a small separation of the skin edges to complete opening that exposes deeper tissues. Causes include mechanical stress or tension on the wound, infection, poor blood supply, certain medications, smoking, uncontrolled diabetes, obesity, or inadequate surgical technique; in severe cases dehiscence may be associated with evisceration when internal organs are exposed.
Management depends on the severity and underlying cause and may include wound cleaning, dressings, antibiotics if infection is present, removal of compromised sutures, negative-pressure wound therapy, or surgical revision to reclose the wound. Preventive measures and recovery-focused care include optimizing nutrition, controlling chronic conditions, stopping smoking, careful wound monitoring for signs like increasing pain or drainage, and prompt medical evaluation to reduce the risk of complications and support proper healing.